Memory, Learning and Sunlight: A new brain paradigm

Memory becomes a worry as humans age, and that worry has spawned a plethora of new anti-forgetfulness products. Based on recent research, we elucidate the manner in which sunlight stimulation of skin may influence important chemical reactions. These reactions improve memory and cognition.
For the purpose of this article, it is necessary to understand the meaning of three terms:
- Urocanic acid (UCA): a crystalline acid normally present in human skin, it may play a part in skin protection.
- Histidine: a basic amino acid that acts as an intermediary between UCA and glutamate
- Glutamate: a chemical that functions as a neurotransmitter and excites cells of the central nervous system
You are probably already forming your own opinion regarding the interaction of sunlight and memory. Let us expatiate on that interaction and unravel a hitherto unknown mystery.
The authors of the aforementioned research noted that seasons of sunlight associated with moderate improvement to physical and mental states. Some conditions you may be familiar with, because we have discussed them at length in these blogs. A few of them are seasonal affective disorder (SAD), bipolar disorder, and depression. Nevertheless, what makes the research so interesting is that it sought answers regarding why sunlight seemed to enhance learning and memory. Moreover, it found a brand new answer.
Because the researchers explored brain neurons to unlock the mystery, they found that UCA existed in many brain regions. This was not something that they had encountered previously, and thus it piqued their curiosity. No other investigators had reported finding UCA in the central nervous system. Yet, they knew UCA was prevalent in skin. Therefore, knowing that sun exposure to the skin produced many photoproducts, they tested a new hypothesis. That hypothesis was that UCA produced by sunlight could be the link that ties sunlight to memory.
How the researchers conducted the experiment
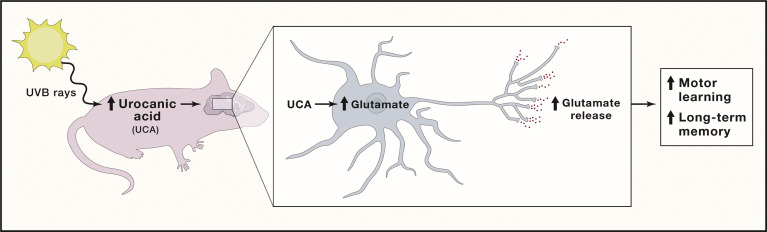
After exposing rats to low-dose UVB exposure (similar to sunlight or sunbed exposure), they observed increased UCA levels in the serum. Moreover, they observed the same increase in UCA levels within the neurons (nerve cells) of the cerebrospinal fluid. Furthermore, they were able to produce the same increases in UCA brain levels by intravenous injection of UCA. This suggests that UCA may cross the blood/brain barrier and enter brain neurons. The authors of the above-cited research stated that UCA is an intermediate part of a conversion of histidine to glutamate. The following graph describes the sunlight>UCA>glutamine>memory connection. (from the authors)
Glutamate, as mentioned, excites neurons in the brain. What better way to improve memory?
To test their hypothesis with “mouse memory,” the investigators assessed the ability of the animals to stay on a moving device called a rotarod. In addition, they observed that administration of both UCA and UV exposure enhanced the performance of the animals.
The bottom line regarding sunlight and brain function
Sun exposure improves memory, and UCA (with glutamate) appears to be one of the mechanisms responsible for that improvement.
Happy sunning!
SmartTan.com news articles regularly report medical and scientific information to keep you abreast of current events related to UV light. This information is not intended to be used by any party to make unwarranted health claims to promote sunbed usage. Indoor tanning businesses are obligated to communicate a fair and balanced message to all clients about your products and services including the potential risks associated with indoor tanning. Contact your Smart Tan representative to find out more about what you can and can’t say in your tanning salon business.
© 2024 International Smart Tan Network. All rights reserved.